Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
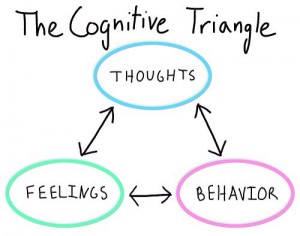
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a time-limited, evidence-based, psychotherapeutic approach that aims to influence dysfunctional cognitions, emotions, and behaviors through a goal-oriented, systematic procedure.
CBT was primarily developed through a merging of behavior therapy and cognitive therapy. These two traditions found common ground in focusing on the “here and now” and symptom removal.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is based on the idea that our thoughts cause our feelings and behaviors, not external factors, like people, events, and situations. The benefit of this is that we can change the way we think, feel, or behave even if the situation does not change.
CBT treatments have received empirical support for effective treatment of a variety of clinical conditions, such as depression, anxiety, eating disorders, sleep disorders, relationship difficulties, and many others.
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) utilizes traditional cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) methods with additional strategies, like mindfulness and mindfulness meditation to deal with psychological disorders.
Mindfulness and mindfulness meditation focus on becoming aware of all incoming thoughts and feelings and accepting them, but not reacting or attaching to them. The goal of MBCT is to interrupt automatic processes that lead to undesired states of mind and, in turn, teach patients to focus less on reacting to incoming stimuli and instead on accepting and observing them without judgment. This mindfulness practice allows the participant to notice when automatic processes are occurring and to alter their reaction to be one more of reflection